
Breaking News
 EXCLUSIVE: "The HUGE Elephant In The Room Is Actually What Jeffrey Epstein Was Best At..."
EXCLUSIVE: "The HUGE Elephant In The Room Is Actually What Jeffrey Epstein Was Best At..."
 EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEW: Republican Candidate For Texas Governor "Doc" Pete Chambers Joins...
EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEW: Republican Candidate For Texas Governor "Doc" Pete Chambers Joins...
 Epstein Files Trigger Political Fallout Across Europe
Epstein Files Trigger Political Fallout Across Europe
 Conjoined twin 'influencers' who have gained more than 280,000 followers with their intimate
Conjoined twin 'influencers' who have gained more than 280,000 followers with their intimate
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Fish-inspired robots coordinate movements without any outside control
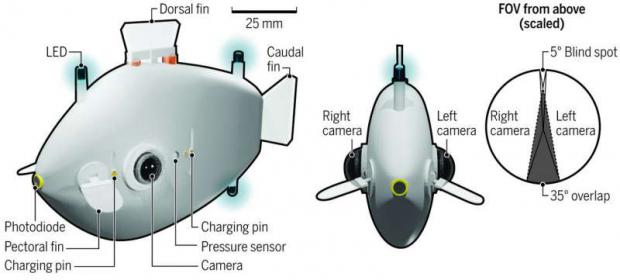
"Robots are often deployed in areas that are inaccessible or dangerous to humans, areas where human intervention might not even be possible," said Florian Berlinger, a Ph.D. Candidate at SEAS and Wyss and first author of the paper. "In these situations, it really benefits you to have a highly autonomous robot swarm that is self-sufficient. By using implicit rules and 3-D visual perception, we were able to create a system that has a high degree of autonomy and flexibility underwater where things like GPS and WiFi are not accessible."



