
Breaking News
 Closing in on How Charlie Kirk Was Assassinated
Closing in on How Charlie Kirk Was Assassinated
 Here's a little song I just wrote. Dedicated to Al Gore.
Here's a little song I just wrote. Dedicated to Al Gore.
 Judge Blocks Executive Order Tightening Voter-registration Requirements
Judge Blocks Executive Order Tightening Voter-registration Requirements
 ALEX JONES' EXCLUSIVE EPSTEIN DOJ MEGA DOCUMENT DUMP ANALYSIS:
ALEX JONES' EXCLUSIVE EPSTEIN DOJ MEGA DOCUMENT DUMP ANALYSIS:
Top Tech News
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
 Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
 New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
 Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Breakthrough Electronic Amoeba Analog Computer For Approximate Solving Traveling Salesman Problems
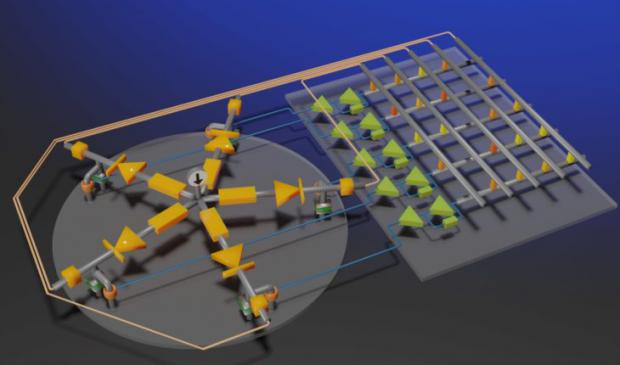
The salesman problem is this question: "Given a list of cities and the distances between each pair of cities, what is the shortest possible route that visits each city exactly once and returns to the origin city?". Having really good solutions for this class of problems means the US postal service, Fedex, UPS, airlines and the US military would save huge amounts of money. It is an NP-hard problem in combinatorial optimization, important in theoretical computer science and operations research.
Conventional digital computers, including supercomputers, are inadequate to solve these complex problems in practically permissible time as the number of candidate solutions they need to evaluate increases exponentially with the problem size. This is a combinatorial explosion. D-Wave Systems and others have created "Ising machines" and "quantum annealers," have been actively developed in recent years. There is complicated pre-processing to convert each task to the form they can handle and have a risk of presenting illegal solutions that do not meet some constraints and requests, resulting in major obstacles to the practical applications.
Approximation Algorithms
Various heuristics and approximation algorithms, which quickly yield good solutions, have been devised. These include the Multi-fragment algorithm. Modern methods can find solutions for extremely large problems (millions of cities) within a reasonable time which are with a high probability just 2–3% away from the optimal solution.
Exact algorithms
The most direct solution would be to try all permutations (ordered combinations) and see which one is cheapest (using brute-force search). The running time for this approach lies within a polynomial factor of {displaystyle O(n!)}O(n!), the factorial of the number of cities, so this solution becomes impractical even for only 20 cities.



