
Breaking News
 One company does over 50% of all school photos in America and over 25% of school photos globally
One company does over 50% of all school photos in America and over 25% of school photos globally
 Your Water Filter Will Clog - The Medieval Sand Filtration System That Purifies Forever
Your Water Filter Will Clog - The Medieval Sand Filtration System That Purifies Forever
 Aaron Day - BTC and Stable Coins: 'The Creature From Epstein Island' (Publisher Recommended)
Aaron Day - BTC and Stable Coins: 'The Creature From Epstein Island' (Publisher Recommended)
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Most Brain Aging Decline Can Be Fixed Overnight
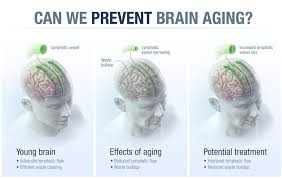
A new University of San Francisco antiaging drug, called ISRIB, has already been shown in laboratory studies to restore memory function months after traumatic brain injury (TBI), reverse cognitive impairments in Down Syndrome, prevent noise-related hearing loss, fight certain types of prostate cancer, and even enhance cognition in healthy animals.
The extremely rapid effects prove that a significant amount of age-related cognitive losses is caused by a kind of reversible physiological blockage rather than more permanent degradation.
ISRIB, discovered in 2013 in Peter Walter's lab, works by rebooting cells' protein production machinery after it gets throttled by one of these stress responses – a cellular quality control mechanism called the integrated stress response (ISR; ISRIB stands for ISR InhiBitor).
Improves Cognition, Boosts Neuron and Immune Cell Function
In the new study, researchers led by Rosi lab postdoc Karen Krukowski, PhD, trained aged animals to escape from a watery maze by finding a hidden platform, a task that is typically hard for older animals to learn. But animals who received small daily doses of ISRIB during the three-day training process were able to accomplish the task as well as youthful mice, much better than animals of the same age who didn't receive the drug.

 Why We'll Win
Why We'll Win
 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

