
Breaking News
 One company does over 50% of all school photos in America and over 25% of school photos globally
One company does over 50% of all school photos in America and over 25% of school photos globally
 Your Water Filter Will Clog - The Medieval Sand Filtration System That Purifies Forever
Your Water Filter Will Clog - The Medieval Sand Filtration System That Purifies Forever
 Aaron Day - BTC and Stable Coins: 'The Creature From Epstein Island' (Publisher Recommended)
Aaron Day - BTC and Stable Coins: 'The Creature From Epstein Island' (Publisher Recommended)
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Inexpensive antivenom could reportedly be used by "anyone, anywhere
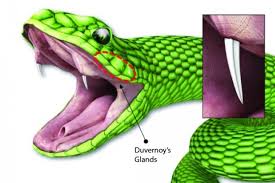
Traditionally, antivenom is produced by first "milking" venom from the fangs of captive snakes, then injecting small amounts of that venom into animals such as horses. Those creatures respond by producing venom-neutralizing antibodies which are harvested from their blood, purified, then used in the antivenom.
This can be quite a lengthy process, plus the workers who extract the venom run a risk of getting bitten by the snakes. Additionally, the antivenom must be applied intravenously, typically in a hospital or clinic

 Why We'll Win
Why We'll Win
 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

