
Breaking News
 One company does over 50% of all school photos in America and over 25% of school photos globally
One company does over 50% of all school photos in America and over 25% of school photos globally
 Your Water Filter Will Clog - The Medieval Sand Filtration System That Purifies Forever
Your Water Filter Will Clog - The Medieval Sand Filtration System That Purifies Forever
 Aaron Day - BTC and Stable Coins: 'The Creature From Epstein Island' (Publisher Recommended)
Aaron Day - BTC and Stable Coins: 'The Creature From Epstein Island' (Publisher Recommended)
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Regenerative drug summons stem cells for inflammation-free healing
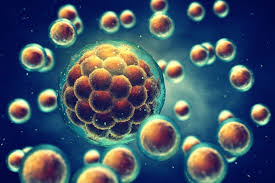
The technique could be a boon for regenerative medicine to treat neurological disorders.
Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury and damage, swelling up to allow better blood flow to the area. It also acts like a "fire alarm" to attract the attention of the immune system to help the healing process, and stem cells are some of the most important responders.
In theory, inflammation could be used to lure these regenerative stem cells to injuries, but of course there are risks. Chronic inflammation underlies conditions like arthritis, multiple sclerosis and Crohn's disease, and has even been linked to cardiovascular diseases, Alzheimer's and depression.
So for the new study, the researchers investigated ways to summon stem cells using inflammation signals without creating further inflammation. The team modified an inflammatory molecule called CXCL12, which had previously been identified as a stem cell attractor. They found that it contains two "pockets" – one that binds to stem cells and one for inflammatory signaling – so they developed a drug that maximizes the binding but minimizes the signaling.
The end result is a drug they call SDV1a, which is designed to be injected almost anywhere in the body to lure stem cells there to begin healing an injury, without causing inflammation.

 Why We'll Win
Why We'll Win
 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

