
Breaking News
 Closing in on How Charlie Kirk Was Assassinated
Closing in on How Charlie Kirk Was Assassinated
 Here's a little song I just wrote. Dedicated to Al Gore.
Here's a little song I just wrote. Dedicated to Al Gore.
 Judge Blocks Executive Order Tightening Voter-registration Requirements
Judge Blocks Executive Order Tightening Voter-registration Requirements
 ALEX JONES' EXCLUSIVE EPSTEIN DOJ MEGA DOCUMENT DUMP ANALYSIS:
ALEX JONES' EXCLUSIVE EPSTEIN DOJ MEGA DOCUMENT DUMP ANALYSIS:
Top Tech News
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
 Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
 New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
 Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Microwave Water Splitting for Breakthroughs for Making Hydrogen, Oxygen and Fast Battery
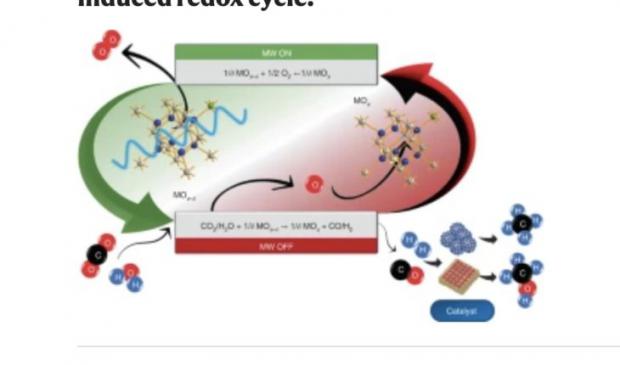
Researchers from the Polytechnic University of Valencia and the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) report contactless H2 production via water electrolysis mediated by the microwave-triggered redox activation of solid-state ionic materials at low temperatures (less than 250 °C).
This will simplify and significantly cheapen the process for hydrogen production.
Water was reduced via reaction with non-equilibrium gadolinium-doped CeO2 that was previously in situ electrochemically deoxygenated by the sole application of microwaves. The microwave-driven reduction was identified by an instantaneous electrical conductivity rise and O2 release. This process was cyclable, whereas H2 yield and energy efficiency were material- and power-dependent. Deoxygenation of low-energy molecules (H2O or CO2) led to the formation of energy carriers and enabled CH4 production when integrated with a Sabatier reactor. This method could be extended to other reactions such as intensified hydrocarbons synthesis or oxidation.



