
Breaking News
 Joe rogan reacts to the Godfather of Ai Geoffrey Hinton talk of his creation
Joe rogan reacts to the Godfather of Ai Geoffrey Hinton talk of his creation
 Shocking Scenes in Russia: Apartment Buildings Buried Under Massive Snowfall!
Shocking Scenes in Russia: Apartment Buildings Buried Under Massive Snowfall!
 Bill Hemmer: THIS is why Greenland matters
Bill Hemmer: THIS is why Greenland matters
 Trump Blasts Britain Over Deal To Return Diego Garcia
Trump Blasts Britain Over Deal To Return Diego Garcia
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
Gryphon Technologies to develop nuclear rocket engine for DARPA
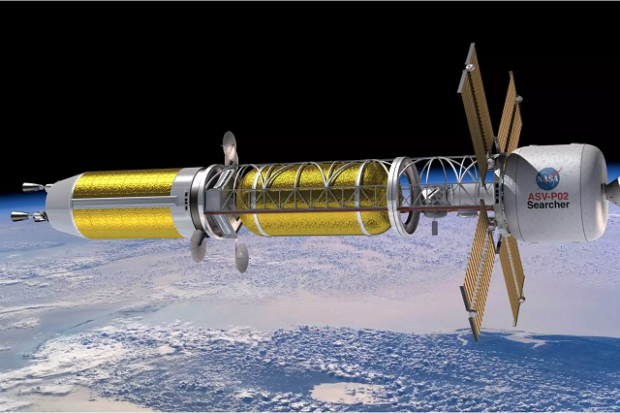
DARPA has awarded a US$14-million contract to the Gryphon Technologies engineering firm to develop and demonstrate a nuclear rocket engine for the agency's Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations (DRACO) program. The High-Assay Low Enriched Uranium (HALEU) Nuclear Thermal Propulsion (NTP) system will allow the US military to carry out missions in cislunar space.
The single greatest limitation in space travel is the propulsion system. On Earth, it's possible to create motors that have a very high payload ratio, so one can, in the words of an early aviator, make a tea tray fly by putting enough power behind it. However, getting into space requires such high velocities and such high energies that engineers are forced to use very large engines and huge amounts of fuel to put very small payloads into orbit.
Once in space, there are essentially two options. One is to use chemical rockets, but these have largely reached their theoretical limits when it comes to thrust, or eclectic propulsion systems that produce very small thrust for very long periods of time.
As far back as 1945, it was recognized that there was a third option, which is to harness the power of the atom to produce a rocket that is more powerful than its chemical counterparts. The problem has been to create a practical design that produces enough thrust to warrant the investment.

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


