
Breaking News
 Kid Rock Responds After He Wins the Internet With a New Song Paying Tribute to Jesus and the Bible
Kid Rock Responds After He Wins the Internet With a New Song Paying Tribute to Jesus and the Bible
 A New Low for the NFL: Bad Bunny Featured Two Men Simulating Sex, Dry Humping During...
A New Low for the NFL: Bad Bunny Featured Two Men Simulating Sex, Dry Humping During...
 This Is BIG…If It Actually Passes | Riley Moore #469 | The Way I Heard It
This Is BIG…If It Actually Passes | Riley Moore #469 | The Way I Heard It
 Tokenized Gold vs The Bitcoin Standard: Peter Schiff debates Saifedean Ammous
Tokenized Gold vs The Bitcoin Standard: Peter Schiff debates Saifedean Ammous
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Cellular aging 'master circuit' discovered: Extended human lifespan to follow?
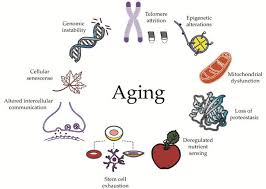
It's a loaded question, strife with philosophical, religious, and societal considerations. Humans have pondered the possibilities of extended, or even immortal, life for as long as we've inhabited this planet. But at the end of the day it's all just a daydream, right?
Not necessarily, according to new research out of the University of California, San Diego. The study, led by UCSD molecular biologists and bioengineers, produced a groundbreaking discovery regarding the intricacies of cellular aging. In light of their findings, researchers say the notion of "dramatically" extending human life isn't so farfetched after all.
Each human's lifespan and personal rate of aging is determined by the aging of their individual cells. Originally, the study's authors just wanted to investigate if different types of cells age at different speeds based on different stimuli/causes. To that end, they studied aging in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

