
Breaking News
 Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
 Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
 Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
 U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Injection of nanoparticle-based retina restores vision to blind rats
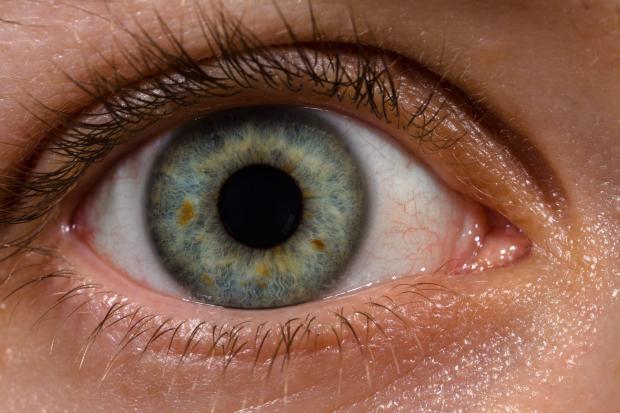
A single injection of nanoparticles was found to create a working artificial retina, restoring vision to blind rodents.
Degenerative age-related vision loss is so common it would be easy to think it simply an unavoidable consequence of getting older. However, a number of innovative research projects have found ways to prevent, or at least slow, this seemingly inevitable process.
A great deal of age-related vision loss is related to a degradation of the retina, so many researchers have worked to develop different kinds of artificial retinas, using electrodes and sensors to replicate retinal functions. However, these prosthetic solutions are not ideal, requiring wiring, cameras and invasive surgery.
Another option to restore retinal function is by using specifically engineered nanoparticles to serve as light-sensitive conduits to retinal neurons. In a newly published study, researchers have demonstrated how conjugated polymer nanoparticles (P3HT-NP) can potentially spread broadly across the sub-retinal space and restore lost vision.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

