
Breaking News
 Kid Rock Responds After He Wins the Internet With a New Song Paying Tribute to Jesus and the Bible
Kid Rock Responds After He Wins the Internet With a New Song Paying Tribute to Jesus and the Bible
 A New Low for the NFL: Bad Bunny Featured Two Men Simulating Sex, Dry Humping During...
A New Low for the NFL: Bad Bunny Featured Two Men Simulating Sex, Dry Humping During...
 This Is BIG…If It Actually Passes | Riley Moore #469 | The Way I Heard It
This Is BIG…If It Actually Passes | Riley Moore #469 | The Way I Heard It
 Tokenized Gold vs The Bitcoin Standard: Peter Schiff debates Saifedean Ammous
Tokenized Gold vs The Bitcoin Standard: Peter Schiff debates Saifedean Ammous
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Neurobiologists Actually Managed to Reverse Stroke Damage Using Human Skin Cells
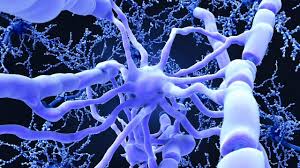
"Six months after the transplantation, we could see how the new cells had repaired the damage that a stroke had caused in the rats' brains," says Professor Zaal Kokaia, one of the researchers behind the study.
Several previous studies from the Lund team and others have shown that it is possible to transplant nerve cells derived from human stem cells or from reprogrammed cells into brains of rats afflicted by stroke. However, it was not known whether the transplanted cells can form connections correctly in the rat brain in a way that restores normal movement and feeling.
"We have used tracking techniques, electron microscopy and other methods, such as light to switch off activity in the transplanted cells, as a way to show that they really have connected correctly in the damaged nerve circuits. We have been able to see that the fibers from the transplanted cells have grown to the other side of the brain, the side where we did not transplant any cells, and created connections. No previous study has shown this," says Kokaia, who—even though he and colleague senior professor Olle Lindvall have studied the brain for several decades—was surprised by the results.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

