
Breaking News
 Palantir kills people? But Who's Really Pushing the Buttons?
Palantir kills people? But Who's Really Pushing the Buttons?
 'Big Short' investor Michael Burry sounds alarm on AI bubble that's 'too big to save
'Big Short' investor Michael Burry sounds alarm on AI bubble that's 'too big to save
 Joe rogan reacts to the Godfather of Ai Geoffrey Hinton talk of his creation
Joe rogan reacts to the Godfather of Ai Geoffrey Hinton talk of his creation
 Shocking Scenes in Russia: Apartment Buildings Buried Under Massive Snowfall!
Shocking Scenes in Russia: Apartment Buildings Buried Under Massive Snowfall!
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
"Quantum radar" uses entangled photons to detect objects
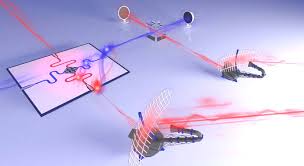
Quantum entanglement describes the bizarre state where two particles can become linked so tightly that they seem to communicate instantly, no matter how far apart they are. Measuring the state of one particle will instantly change the state of the other, hypothetically even if it's on the other side of the universe. That implies that the information is moving faster than the speed of light, which is thought to be impossible – and yet, it's clearly and measurably happening. The phenomenon even unnerved Einstein himself, who famously described it as "spooky action at a distance."
While we still don't entirely understand why or how it works, that's not stopping scientists figuring out ways to use it to our advantage. Strides are being made towards creating quantum computers and a quantum internet, both of which would be super fast and nigh-unhackable. And now, in a new study by physicists at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (IST Austria), MIT and the University of York, the phenomenon been applied to radar.

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


