
Breaking News
 Windows 10 is DEAD in 2025? -- Here's How I Run It SAFELY Forever (No Updates)
Windows 10 is DEAD in 2025? -- Here's How I Run It SAFELY Forever (No Updates)
 GENIUS ACT TRIGGERED: The Biggest BANK RUN in History is COMING – Prepare NOW
GENIUS ACT TRIGGERED: The Biggest BANK RUN in History is COMING – Prepare NOW
 European Billionaires Funneled $2 Billion into NGO Network to Fund Anti-Trump Protest Machine
European Billionaires Funneled $2 Billion into NGO Network to Fund Anti-Trump Protest Machine
 Japan Confirms Over 600,000 Citizens Killed by COVID mRNA 'Vaccines'
Japan Confirms Over 600,000 Citizens Killed by COVID mRNA 'Vaccines'
Top Tech News
 HUGE 32kWh LiFePO4 DIY Battery w/ 628Ah Cells! 90 Minute Build
HUGE 32kWh LiFePO4 DIY Battery w/ 628Ah Cells! 90 Minute Build
 What Has Bitcoin Become 17 Years After Satoshi Nakamoto Published The Whitepaper?
What Has Bitcoin Become 17 Years After Satoshi Nakamoto Published The Whitepaper?
 Japan just injected artificial blood into a human. No blood type needed. No refrigeration.
Japan just injected artificial blood into a human. No blood type needed. No refrigeration.
 The 6 Best LLM Tools To Run Models Locally
The 6 Best LLM Tools To Run Models Locally
 Testing My First Sodium-Ion Solar Battery
Testing My First Sodium-Ion Solar Battery
 A man once paralyzed from the waist down now stands on his own, not with machines or wires,...
A man once paralyzed from the waist down now stands on his own, not with machines or wires,...
 Review: Thumb-sized thermal camera turns your phone into a smart tool
Review: Thumb-sized thermal camera turns your phone into a smart tool
 Army To Bring Nuclear Microreactors To Its Bases By 2028
Army To Bring Nuclear Microreactors To Its Bases By 2028
 Nissan Says It's On Track For Solid-State Batteries That Double EV Range By 2028
Nissan Says It's On Track For Solid-State Batteries That Double EV Range By 2028
Soft-bodied robot channels the cheetah to move fast
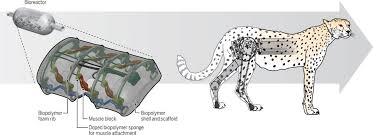
The world's fastest land animal, cheetahs run by rapidly flexing their spines between two stable states. A consortium of American scientists recently set out to replicate that motion in a soft robot. The resulting device is known as LEAP, which stands for "Leveraging Elastic instabilities for Amplified Performance."
Instead of muscles and a biological spine, the silicone-bodied robot incorporates two soft pneumatic actuators and a flexible spring-loaded mechanical spine. Alternately pumping air in and out of the two actuators causes energy to be stored and suddenly released, triggering the spring to instantly flex the spine from one stable state to another. As a result, the bot is able to exert force against the ground, leaping off of it.
Utilizing this technique, LEAP is able to gallop at a rate of up to 2.7 body lengths per second across flat, solid surfaces.

 Carbon based computers that run on iron
Carbon based computers that run on iron

