
Breaking News
 Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
 Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
 Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
 U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Handheld 3D printer used to grow replacement muscle tissue
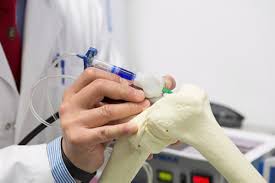
We've actually been hearing a lot about "bioscaffolds" lately.
In a nutshell, they're three-dimensional pieces of biocompatible material that are implanted within the body, and that have a microstructure similar to that of the surrounding tissue. Over time, cells from that tissue migrate into the scaffold, colonizing it and reproducing. Eventually, they entirely replace the material, forming pure muscle, bone, cartilage or other tissue.
That said, pre-producing such bioscaffolds and then implanting them in muscle is quite challenging. With that in mind, scientists at the University of Connecticut developed a prototype handheld 3D printer to do the job.
It starts by depositing a gelatin-based hydrogel directly into the unwanted gap within the muscle. An integrated ultraviolet light causes that gel to cure into a bioscaffold made up of tiny muscle-like fibers, which readily adheres to the adjacent muscle tissue – no sutures are required. Muscle cells then move into the scaffolding.
In lab tests, the device proved to be effective at treating volumetric muscle loss injuries in mice.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

