
Breaking News
 This roof paint blocks 97% of sunlight and pulls water from the air
This roof paint blocks 97% of sunlight and pulls water from the air
 'Venomous' Republican split over Israel hits new low as fiery feud reaches White House
'Venomous' Republican split over Israel hits new low as fiery feud reaches White House
 Disease-ridden monkey that escaped from research facility shot dead by vigilante mom protecting...
Disease-ridden monkey that escaped from research facility shot dead by vigilante mom protecting...
 Hooters returns - founders say survival hinges on uniform change after buying chain...
Hooters returns - founders say survival hinges on uniform change after buying chain...
Top Tech News
 The 6 Best LLM Tools To Run Models Locally
The 6 Best LLM Tools To Run Models Locally
 Testing My First Sodium-Ion Solar Battery
Testing My First Sodium-Ion Solar Battery
 A man once paralyzed from the waist down now stands on his own, not with machines or wires,...
A man once paralyzed from the waist down now stands on his own, not with machines or wires,...
 Review: Thumb-sized thermal camera turns your phone into a smart tool
Review: Thumb-sized thermal camera turns your phone into a smart tool
 Army To Bring Nuclear Microreactors To Its Bases By 2028
Army To Bring Nuclear Microreactors To Its Bases By 2028
 Nissan Says It's On Track For Solid-State Batteries That Double EV Range By 2028
Nissan Says It's On Track For Solid-State Batteries That Double EV Range By 2028
 Carbon based computers that run on iron
Carbon based computers that run on iron
 Russia flies strategic cruise missile propelled by a nuclear engine
Russia flies strategic cruise missile propelled by a nuclear engine
 100% Free AC & Heat from SOLAR! Airspool Mini Split AC from Santan Solar | Unboxing & Install
100% Free AC & Heat from SOLAR! Airspool Mini Split AC from Santan Solar | Unboxing & Install
 Engineers Discovered the Spectacular Secret to Making 17x Stronger Cement
Engineers Discovered the Spectacular Secret to Making 17x Stronger Cement
Could This Liquid Lithium Li-S Battery Have Automotive Applications?
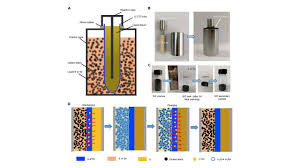
We have covered lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries quite often here at InsideEVs, but never one like this. These batteries use solid lithium as anodes and liquid organic electrolytes, but what if the electrolyte was solid and the lithium was liquid? That is what researchers from the Zhengzhou University, Tsinghua University, and Stanford University have proposed.These batteries, using sulfur or selenium, avoid the growth of lithium dendrites and have high Coulombic efficiency and cycling stability, according to the researchers. All due to the way they work.
The batteries operate at temperatures above lithium melting point, at 180.5ºC (356.9ºF. We'd bet on something around 200ºC (392ºF). This liquid lithium is then stored inside the solid electrolyte, a ceramic tube made of LLZTO (Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12).



