
Breaking News
 Full-Out, Digitized Technocratic Rule Is Not Around The Corner, It Is Next Door
Full-Out, Digitized Technocratic Rule Is Not Around The Corner, It Is Next Door
 Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
 Hormuz Is Closing -- Oil Skyrockets. Food and Chips Are Next...
Hormuz Is Closing -- Oil Skyrockets. Food and Chips Are Next...
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Laser-driven Particle Accelerator Made Ten Thousand Times Smaller
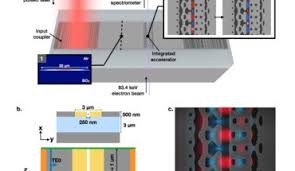
Current implementations of DLAs rely on free-space lasers directly incident on the accelerating structures, limiting the scalability and integrability of this technology. Researchers present the first experimental demonstration of a waveguide-integrated DLA, designed using a photonic inverse design approach. These on-chip devices accelerate sub-relativistic electrons of initial energy 83.4 keV by 1.21 keV over 30 µm, providing peak acceleration gradients of 40.3 MeV/m. This progress represents a significant step towards a completely integrated MeV-scale dielectric laser accelerator.
Dielectric laser accelerators have emerged as a promising alternative to conventional RF accelerators due to the large damage threshold of dielectric materials the commercial availability of powerful NIR femtosecond pulsed lasers, and the low-cost high-yield nanofabrication processes which produce them. Together, these advantages allow DLAs to make an impact in the development of applications such as tabletop free-electron-lasers, targeted cancer therapies, and compact imaging sources.

 Going Down with the Ship
Going Down with the Ship


