
Breaking News
 Bret Weinstein's Thoughts on Charlie Kirk and Iran
Bret Weinstein's Thoughts on Charlie Kirk and Iran
 We Are the Villains in This Story
We Are the Villains in This Story
 My Prediction For the War with Iran
My Prediction For the War with Iran
 Foreign Hacker Cracked Into FBI's Epstein Files In 2023, Was 'Disgusted' At Child Sexual
Foreign Hacker Cracked Into FBI's Epstein Files In 2023, Was 'Disgusted' At Child Sexual
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Metallic Wood: New Material That Is As Strong As Titanium But 5 Times Lighter
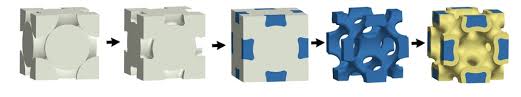
Although it's not a new element and basically consists of nickel, it is four to five times lighter than titanium thanks to its unique porous construction which is similar to natural materials such as wood: hence the name Metallic Wood.
The study was led by James Pikul, Assistant Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics at Penn Engineering. Here is what he had to say about this material:
The reason we call it metallic wood is not just its density, which is about that of wood, but its cellular nature. Cellular materials are porous; if you look at wood grain, that's what you're seeing — parts that are thick and dense and made to hold the structure, and parts that are porous and made to support biological functions, like transport to and from cells.
Our structure is similar. We have areas that are thick and dense with strong metal struts, and areas that are porous with air gaps. We're just operating at the length scales where the strength of struts approaches the theoretical maximum.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

