
Breaking News
 Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
 Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
 Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
 U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Nobel-winning technology reveals cancer-killing virus locking onto target like a "key in a lock
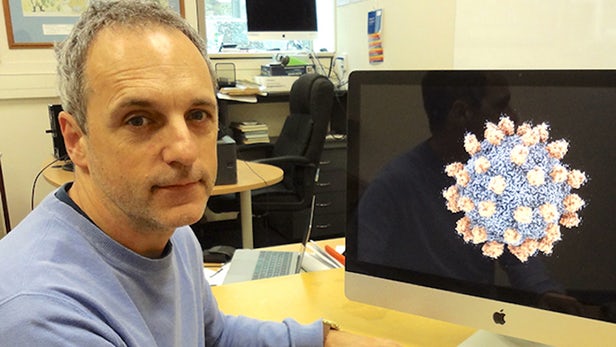
Last year, a cutting edge scientific imaging technology called cryo-electron microscopy earned a Nobel Prize for chemistry, lauded by the committee as ushering in a "revolution in biochemistry." The technique allows scientists to visualize biomolecules in their natural state for the first time ever, and one year on is already opening up some exciting possibilities. Now, scientists have used it to image a high-potential cancer-killing virus in unprecedented detail, allowing them to now ponder how it might be genetically modified to better do the job.
According to the Nobel statement accompanying the announcement last year, cryo-electron microscopy has allowed scientists to "visualise processes they have never previously seen." It relies on a careful freezing method that turns water inside cells into a solid to preserve their cellular structure, along with a modified electron microscope that blasts it with weakened beams for that very same reason.
This, paired with pioneering mathematical algorithms, has already enabled scientists to use cryo-electron microscopy to probe the secrets of poisonous bacteria, polio-fighting plant viruses and the immune-regulating effects of tick saliva. Now, scientists at the University of Otago and the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) are using it to explore the potential for designer viruses that kill off cancer.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

