
Breaking News
 The Pentagon Failed Its Audit Again. You Should Be Alarmed.
The Pentagon Failed Its Audit Again. You Should Be Alarmed.
 Cuban Crisis 2.0. What if 'Gerans' flew from Cuba?
Cuban Crisis 2.0. What if 'Gerans' flew from Cuba?
 Senate Democrats Offer Promising Ideas for Changing Immigration Enforcement
Senate Democrats Offer Promising Ideas for Changing Immigration Enforcement
 Never Seen Risk Like This Before in My Career
Never Seen Risk Like This Before in My Career
Top Tech News
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
 Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
 New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
 Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Electrons that behaves like light in twelve-sided graphene quasicrystal
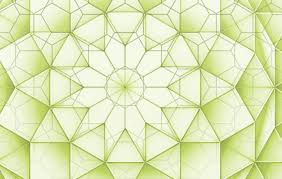
They have useful and unique electronic properties which are useful for probing new physics and they might be useful for spintronics and quantum computers. Those might be far faster forms of computing.
Electrons in monolayer graphene are described by massless Dirac electrons, which exhibit unique quantum phenomena due to the pseudospin and Berry phase of the massless electron.
A tunable bandgap up to 200 meV can be induced in bilayer graphene with electrical gating.
Dirac fermions in quasicrystalline graphene
Quasicrystal lattices, which can have rotational order but lack translational symmetry, can be used to explore electronic properties of materials between crystals and disordered solids. Ahn et al. grew graphene bilayers rotated exactly 30° that have 12-fold rotational order. Electron diffraction and microscopy confirmed the formation of quasicrystals, and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy revealed anomalous interlayer electronic coupling that was quasi-periodic.



