
Breaking News
 Bret Weinstein's Thoughts on Charlie Kirk and Iran
Bret Weinstein's Thoughts on Charlie Kirk and Iran
 We Are the Villains in This Story
We Are the Villains in This Story
 My Prediction For the War with Iran
My Prediction For the War with Iran
 Foreign Hacker Cracked Into FBI's Epstein Files In 2023, Was 'Disgusted' At Child Sexual
Foreign Hacker Cracked Into FBI's Epstein Files In 2023, Was 'Disgusted' At Child Sexual
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Asphalt-lithium metal batteries fully charge in five minutes
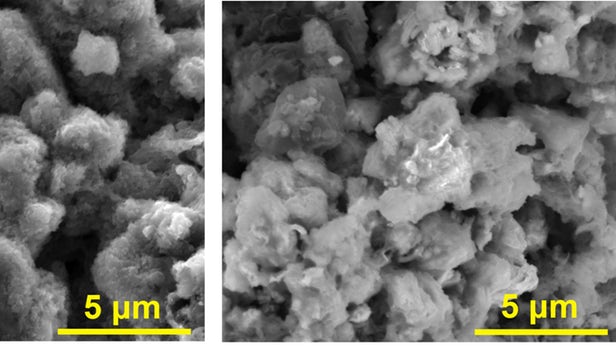
Variations like lithium-air and lithium metal batteries are in the works to possibly replace them, and now researchers at Rice University have improved the latter with the help of an unlikely ingredient. The team found that adding asphalt to the anode made for lithium metal batteries that charge faster and are less likely to short circuit and fail.
To make their new battery, the Rice researchers used untreated gilsonite, a derivative of asphalt, and mixed it with conductive graphene nanoribbons. Then, that composite was coated in lithium metal through the process of electrochemical deposition, to create an anode. The final battery is made by combining this anode with a cathode of sulfurized carbon.
The team tested these new asphalt-lithium metal batteries over more than 500 charge-discharge cycles, and found the porous carbon material from the asphalt made the battery more stable.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

