
Breaking News
 The Pentagon Failed Its Audit Again. You Should Be Alarmed.
The Pentagon Failed Its Audit Again. You Should Be Alarmed.
 Cuban Crisis 2.0. What if 'Gerans' flew from Cuba?
Cuban Crisis 2.0. What if 'Gerans' flew from Cuba?
 Senate Democrats Offer Promising Ideas for Changing Immigration Enforcement
Senate Democrats Offer Promising Ideas for Changing Immigration Enforcement
 Never Seen Risk Like This Before in My Career
Never Seen Risk Like This Before in My Career
Top Tech News
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
 Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
 New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
 Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
A voltage breakthrough with perovskite solar cells to edge closer to commercialization
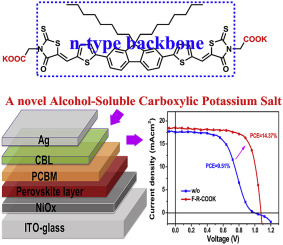
A team of researchers from Peking University and the Universities of Surrey, Oxford and Cambridge detail a new way to reduce an unwanted process called non-radiative recombination, where energy and efficiency is lost in perovskite solar cells.
The team created a technique called Solution-Process Secondary growth (SSG) which increased the voltage of inverted perovskite solar cells by 100 millivolts, reaching a high of 1.21 volts without compromising the quality of the solar cell or the electrical current flowing through a device. They tested the technique on a device which recorded a PCE of 20.9 percent, the highest certified PCE for inverted perovskite solar cells ever recorded.
Researchers are still working towards increasing efficiency and stability, prolonging lifetime and replacing toxic materials with safer ones. Researchers are also looking at the benefits of combining perovskites with other technologies, like silicon for tandem cells.



