
Breaking News
 Bret Weinstein's Thoughts on Charlie Kirk and Iran
Bret Weinstein's Thoughts on Charlie Kirk and Iran
 We Are the Villains in This Story
We Are the Villains in This Story
 My Prediction For the War with Iran
My Prediction For the War with Iran
 Foreign Hacker Cracked Into FBI's Epstein Files In 2023, Was 'Disgusted' At Child Sexual
Foreign Hacker Cracked Into FBI's Epstein Files In 2023, Was 'Disgusted' At Child Sexual
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
"3D battery" design twists together for split-second charging
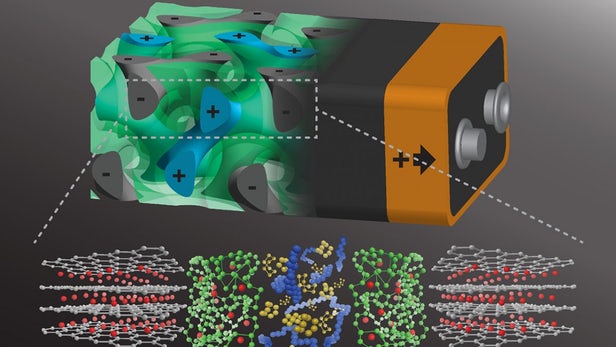
Now, engineers at Cornell University have developed an unusual new structure that intertwines the components together in a swirling shape, which they say lets the device recharge in a matter of seconds.
The Cornell team's new battery architecture is based on a complex, porous shape known as a gyroid, which has previously been used to make the most of the 2D wonder material graphene. The new battery also used thin films of carbon (although not thin enough to become graphene), built into a gyroidal shape using a process known as block co-polymer self-assembly.
This carbon gyroid forms the anode of the battery, and contains thousands of pores each about 40 nanometers wide. These pores were then coated with a separator layer about 10 nanometers thick, and then a sulfur cathode was added. The final ingredient to fill up the last bit of those pores is an electronically-conducting polymer called PEDOT.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

