
Breaking News
 Palantir kills people? But Who's Really Pushing the Buttons?
Palantir kills people? But Who's Really Pushing the Buttons?
 'Big Short' investor Michael Burry sounds alarm on AI bubble that's 'too big to save
'Big Short' investor Michael Burry sounds alarm on AI bubble that's 'too big to save
 2026-01-21 -- Ernest Hancock interviews Professor James Corbett (Corbett Report) MP3&4
2026-01-21 -- Ernest Hancock interviews Professor James Corbett (Corbett Report) MP3&4
 Joe rogan reacts to the Godfather of Ai Geoffrey Hinton talk of his creation
Joe rogan reacts to the Godfather of Ai Geoffrey Hinton talk of his creation
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
ESA Is Building an Air Breathing Space Thruster For Satellites
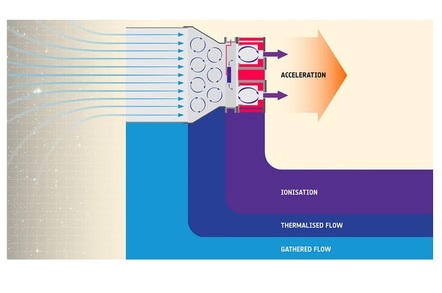
Perhaps outer space's most defining characteristic is the lack of air. The vacuum of space, largely devoid of molecules, makes the European Space Agency's new efforts to build an air-breathing thruster a significant challenge. The space agency recently hit a milestone developing a the new propulsion technology, however, building and testing a thruster in space-like conditions on the ground.
The ESA has been studying air-breathing electric thrusters (ABET) for over a decade. In 2007, a study concluded that the technology "could provide a promising innovative solution" for low Earth orbit (LEO) travel. In this low orbit around the planet, the upper atmosphere is actually thick enough to drag on spacecraft, requiring fuel thrusters to periodically lift satellites to keep them in orbit. An air-breathing thruster could collect these molecules and accelerate them out the back to achieve propulsion, allowing satellites to orbit for longer.

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


