
Breaking News
 The Pentagon Failed Its Audit Again. You Should Be Alarmed.
The Pentagon Failed Its Audit Again. You Should Be Alarmed.
 Cuban Crisis 2.0. What if 'Gerans' flew from Cuba?
Cuban Crisis 2.0. What if 'Gerans' flew from Cuba?
 Senate Democrats Offer Promising Ideas for Changing Immigration Enforcement
Senate Democrats Offer Promising Ideas for Changing Immigration Enforcement
 Never Seen Risk Like This Before in My Career
Never Seen Risk Like This Before in My Career
Top Tech News
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
 Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
 New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
 Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Roll-to-roll chemical vapor deposition system makes long sheets of high quality graphene
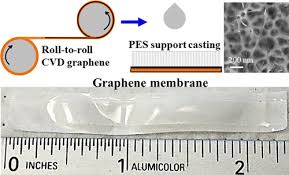
MIT has combined a roll-to-roll approach — a common industrial approach for continuous processing of thin foils — with the common graphene-fabrication technique of chemical vapor deposition, to manufacture high-quality graphene in large quantities and at a high rate.
The system consists of two spools, connected by a conveyor belt that runs through a small furnace. The first spool unfurls a long strip of copper foil, less than 1 centimeter wide. When it enters the furnace, the foil is fed through first one tube and then another, in a "split-zone" design.
While the foil rolls through the first tube, it heats up to a certain ideal temperature, at which point it is ready to roll through the second tube, where the scientists pump in a specified ratio of methane and hydrogen gas, which are deposited onto the heated foil to produce graphene.
"Graphene starts forming in little islands, and then those islands grow together to form a continuous sheet," Hart says. "By the time it's out of the oven, the graphene should be fully covering the foil in one layer, kind of like a continuous bed of pizza."
The researchers found that they were able to feed the foil continuously through the system, producing high-quality graphene at a rate of 5 centimeters per minute. Their longest run lasted almost four hours, during which they produced about 10 meters of continuous graphene.



