
Breaking News
 EXCLUSIVE: "The HUGE Elephant In The Room Is Actually What Jeffrey Epstein Was Best At..."
EXCLUSIVE: "The HUGE Elephant In The Room Is Actually What Jeffrey Epstein Was Best At..."
 EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEW: Republican Candidate For Texas Governor "Doc" Pete Chambers Joins...
EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEW: Republican Candidate For Texas Governor "Doc" Pete Chambers Joins...
 Epstein Files Trigger Political Fallout Across Europe
Epstein Files Trigger Political Fallout Across Europe
 Conjoined twin 'influencers' who have gained more than 280,000 followers with their intimate
Conjoined twin 'influencers' who have gained more than 280,000 followers with their intimate
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Nanoscale "supersoap" allows liquid 3D structures to be printed within other liquids
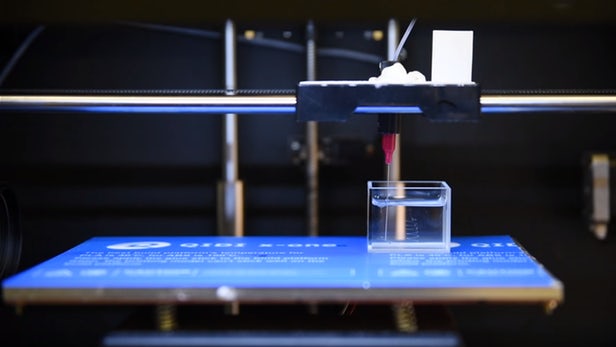
Because of a special nanoscale coating, the water structures survive without breaking down into droplets even as the encapsulating fluid changes shape. This new form of 3D printing could give rise to flexible and stretchable liquid electronics, aid chemical synthesis, or serve as a transport and delivery system for nanoscale particles.
The team of researchers led by Tom Russell modified a standard 3D printer so it would inject narrow streams of water directly into a small container filled with silicon oil. The streams of water don't break down into droplets thanks to a special nanoscale surfactant – a substance that reduces surface tension – which separates the water from the surrounding liquid.
The surfactant, a "nanoparticle supersoap," simultaneously disperses gold nanoparticles into the water and binding polymers into the oil. After water is injected, the polymers attach to individual water molecules, forming a soap, vitrifying, and locking the water structures into place even as the surrounding oil changes shape.



