
Breaking News
 $100 Solar Panel vs $100 Wind Turbine in a Normal Backyard
$100 Solar Panel vs $100 Wind Turbine in a Normal Backyard
 Tucker Carlson on Iran War latest, Trump's MAGA collapse, & Israel's media blackout | Redact
Tucker Carlson on Iran War latest, Trump's MAGA collapse, & Israel's media blackout | Redact
 INDIANA DRAWS THE LINE ON FARMS
INDIANA DRAWS THE LINE ON FARMS
 $35,000 Solar System Cannot Charge to 100%?? Seriously Sol Ark and Deye?
$35,000 Solar System Cannot Charge to 100%?? Seriously Sol Ark and Deye?
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Scientists Discover Hundreds of 2D Materials That Could Be The Next Graphene
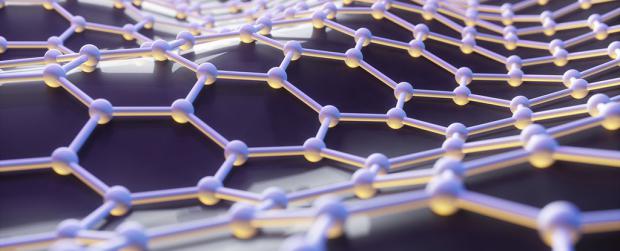
Part of what makes graphene so fantastically useful is its amazing thinness – it's just one atom thick.
Scientists have now found hundreds of other materials that are equally thin, providing a wide selection of new materials with perhaps as much potential as graphene.
The team analysed data in open resources including the Crystallography Open Database, looking for materials with structural similarities to graphene with the help of a custom computer program.
They were looking for materials with strong chemical bonds along one plane – the 2D atom layer – and relatively weak non-chemical action along the perpendicular plane. It's this combination that lets us peel sheets of graphene from graphite.
Starting off with a pool of over 100,000 crystal structures, the team from the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne in Switzerland was able to narrow down the selection to 1,825 compounds with the potential to form sheets just a single atom thick.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

