
Breaking News
 Tuesday War Room LIVE: Trump Set to Shatter Deportation Record by End of First Year…
Tuesday War Room LIVE: Trump Set to Shatter Deportation Record by End of First Year…
 Parallel Polis Reborn: Freeing the Market through Decentralized Technologies
Parallel Polis Reborn: Freeing the Market through Decentralized Technologies
 Amazon goes nuclear with new modular reactor plant
Amazon goes nuclear with new modular reactor plant
 The alarming reality EXPOSED by the global internet meltdown... and why Amazon's crash...
The alarming reality EXPOSED by the global internet meltdown... and why Amazon's crash...
Top Tech News
 3D Printed Aluminum Alloy Sets Strength Record on Path to Lighter Aircraft Systems
3D Printed Aluminum Alloy Sets Strength Record on Path to Lighter Aircraft Systems
 Big Brother just got an upgrade.
Big Brother just got an upgrade.
SEMI-NEWS/SEMI-SATIRE: October 12, 2025 Edition
 Stem Cell Breakthrough for People with Parkinson's
Stem Cell Breakthrough for People with Parkinson's
 Linux Will Work For You. Time to Dump Windows 10. And Don't Bother with Windows 11
Linux Will Work For You. Time to Dump Windows 10. And Don't Bother with Windows 11
 XAI Using $18 Billion to Get 300,000 More Nvidia B200 Chips
XAI Using $18 Billion to Get 300,000 More Nvidia B200 Chips
 Immortal Monkeys? Not Quite, But Scientists Just Reversed Aging With 'Super' Stem Cells
Immortal Monkeys? Not Quite, But Scientists Just Reversed Aging With 'Super' Stem Cells
 ICE To Buy Tool That Tracks Locations Of Hundreds Of Millions Of Phones Every Day
ICE To Buy Tool That Tracks Locations Of Hundreds Of Millions Of Phones Every Day
 Yixiang 16kWh Battery For $1,920!? New Design!
Yixiang 16kWh Battery For $1,920!? New Design!
 Find a COMPATIBLE Linux Computer for $200+: Roadmap to Linux. Part 1
Find a COMPATIBLE Linux Computer for $200+: Roadmap to Linux. Part 1
NASA's X3 ion thruster smashes records in test firings
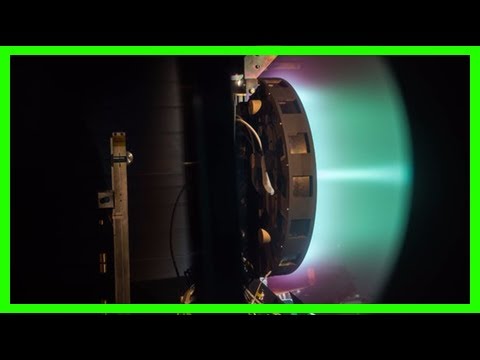
That scenario is now one step closer, as engineers from NASA and the University of Michigan have successfully tested the X3, a thruster designed to get us to Mars. And it's broken several records in the process.
The X3 is one of three Mars engine prototypes currently in development. It is what's known as a Hall thruster, which uses electric and magnetic fields to ionize gases like xenon and expels the ions to produce thrust. The technique is much cleaner, safer and more fuel efficient than traditional chemical rockets, but the trade off is relatively low thrust and acceleration.
"Mars missions are just on the horizon, and we already know that Hall thrusters work well in space," says Alec Gallimore, lead engineer on the X3's development. "They can be optimized either for carrying equipment with minimal energy and propellant over the course of a year or so, or for speed — carrying the crew to Mars much more quickly."



