
Breaking News
 China's Nightmarish New Bio Weapon Targets Race and Ethnicity
China's Nightmarish New Bio Weapon Targets Race and Ethnicity
 The Epstein Files Just EXPOSED the AI Mind Control Agenda (2026 Warning)
The Epstein Files Just EXPOSED the AI Mind Control Agenda (2026 Warning)
 Maxwell offers testimony if granted Trump clemency
Maxwell offers testimony if granted Trump clemency
 How RFK Jr's Guidelines Could Change Farming - Joel Salatin
How RFK Jr's Guidelines Could Change Farming - Joel Salatin
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
AgeX and Insilico reveal genes implicated in tissue regeneration, cancer, and aging
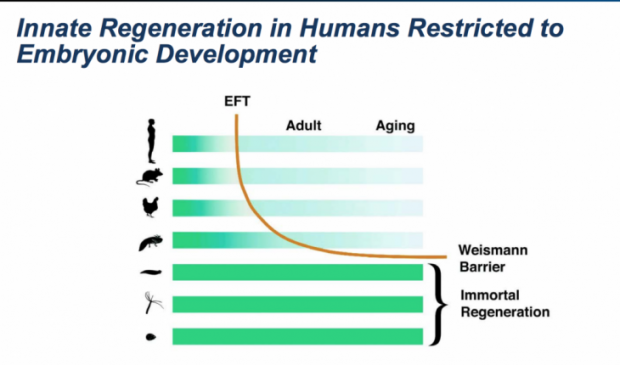
The study, by scientists at AgeX and BioTime, in collaboration with Insilico Medicine, utilized artificial intelligence (AI) technology to parse millions of gene expression data points to decipher the complex mechanisms controlling natural tissue regeneration. The results, published in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Oncotarget, showed that the candidate genes are expressed differently in tissues early in development when they are capable of regeneration compared to later in life when regeneration can no longer take place. Surprisingly, some of the genes, including one highlighted in the study, COX7A1, displayed a rare profile of being nearly universally dysregulated in diverse types of cancer. The discoveries may lead to novel strategies to induce Tissue Regeneration (iTRTM) in the context of trauma or age-related degenerative disease, as well as treat and diagnose cancer.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

