
Breaking News
 Holy Sh*t...Now Deutsche Bank AND Morgan Stanley!?
Holy Sh*t...Now Deutsche Bank AND Morgan Stanley!?
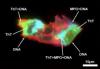 Amyloid microclots were found in 100% of the C-19 inoculated in a new study.
Amyloid microclots were found in 100% of the C-19 inoculated in a new study.
 If The "Iranians" Attack Here…
If The "Iranians" Attack Here…
 Kraken's surprise Fed win may harken onslaught of crypto firms with narrow Fed access
Kraken's surprise Fed win may harken onslaught of crypto firms with narrow Fed access
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Battery Breakthrough May Triple the Range on a Single Charge

Quanan Pang, who led the research while a PhD candidate at Waterloo, and his fellow researchers made a breakthrough involving the use of negative electrodes made of lithium metal. The material has the potential to dramatically increase battery storage technology.
With increased energy density and therefore energy capacity, electric vehicles could see as much as three times the range on a single charge.
"This will mean cheap, safe, long-lasting batteries that give people much more range in their electric vehicles," said Pang.
In developing the technology, two challenges arose for researchers. The first involved a risk of fires and explosions caused by microscopic structural changes to the lithium metal during repeated charge-discharge cycles. The second involved a reaction that creates corrosion and limits both how well the electrodes work and how long they last.
Researchers were able to solve both problems by adding a compound of phosphorus and sulfur to the electrolyte liquid carrying a charge within batteries.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

