
Breaking News
 Israeli Prime Minister, Netanyahu will meet with Trump on Wednesday and deliver instructions...
Israeli Prime Minister, Netanyahu will meet with Trump on Wednesday and deliver instructions...
 Elon Musk Offers To Cover Legal Bills Of Epstein Survivors Who Identify New Names
Elon Musk Offers To Cover Legal Bills Of Epstein Survivors Who Identify New Names
 Red Alert Emergency Broadcast! Tune In NOW As Alex Jones Analyzes The Insane Revelations...
Red Alert Emergency Broadcast! Tune In NOW As Alex Jones Analyzes The Insane Revelations...
 330 gallons of sulphuric acid was purchased for Epstein Island on the day the FBI opened...
330 gallons of sulphuric acid was purchased for Epstein Island on the day the FBI opened...
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Engineered Stem Cells repaired spinal cords in 5 out of 12 Rats
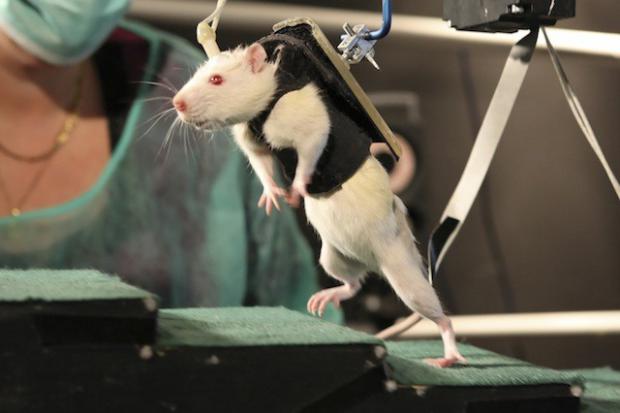
Led by Dr. Shulamit Levenberg, of the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, the researchers implanted human stem cells into rats with a complete spinal cord transection. The stem cells, which were derived from the membrane lining of the mouth, were induced to differentiate into support cells that secrete factors for neural growth and survival.
The work involved more than simply inserting stem cells at various intervals along the spinal cord. The research team also built a three-dimensional scaffold that provided an environment in which the stem cells could attach, grow and differentiate into support cells. This engineered tissue was also seeded with human thrombin and fibrinogen, which served to stabilize and support neurons in the rat's spinal cord.
5 of 12 rats (42%) treated with the induced constructs demonstrated BBB scores exceeding 17, a compiled reflection of improved coordinated gait, plantar placement, weight support, recovery of toe clearance, trunk stability, and predominant parallel paw and tail position, suggesting regained cortical motor control.



