
Breaking News
 RAY DALIO SAYS THE MONETARY ORDER IS BREAKING DOWN...
RAY DALIO SAYS THE MONETARY ORDER IS BREAKING DOWN...
 2026 - The Year US Hegemony Ends?
2026 - The Year US Hegemony Ends?
 Censorship Lawsuit Big Tech Hoped Wouldn't Happen
Censorship Lawsuit Big Tech Hoped Wouldn't Happen
 House Oversight Panel votes to advance contempt resolutions against the Clintons
House Oversight Panel votes to advance contempt resolutions against the Clintons
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
Mars and beyond: Modular nuclear reactors set to power next wave of deep space exploration
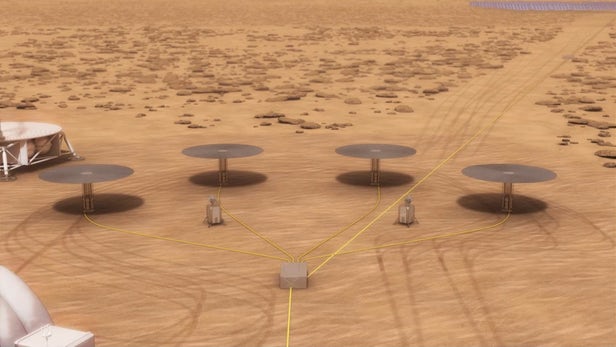
NASA is planning to put astronauts on Mars one day and since the Red Planet is about as off the grid as you can get, the space agency is developing a new generation of modular nuclear reactors to power manned outposts. Under funding from the Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD), the Kilopower project is a multi-year effort to build simple, inexpensive reactors that can be used for a wide variety of planetary and deep space missions.
One of the primary problems with almost any space mission is how to provide it with power. Depending on the goal of the mission and its duration, there are any number of options. The very first satellites used batteries that supplied them with electricity for a few days. Soon, solar panels were added that extended the mission life to years. Fuel cells provided manned missions with not only power, but drinking water as well as hydrogen mingled with oxygen to create electricity and a potable waste product.
Unfortunately, all of these options turned out to be very limited in application. The most successful of them, solar power, only works when sunlight of sufficient brightness shines on the panels. This means that it's a system largely confined to the inner Solar System with Jupiter as the extreme limit, doesn't provide much in the way or power density, is bulky, and is useless at night or on planetary surfaces that may be obscured by dust and clouds.

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


