
Breaking News
 No clear Iran endgame as Trump's position shifts by the hour
No clear Iran endgame as Trump's position shifts by the hour
 US-Israel Iran War Live Updates: US Navy has not escorted any tankers through Strait of Hormuz...
US-Israel Iran War Live Updates: US Navy has not escorted any tankers through Strait of Hormuz...
 Scott Ritter: Iran HITTING US BASES & ISRAEL LIKE NEVER BEFORE, Trump's Oil War Backfires
Scott Ritter: Iran HITTING US BASES & ISRAEL LIKE NEVER BEFORE, Trump's Oil War Backfires
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Could graphene ripples be tapped into as a clean, limitless energy source?
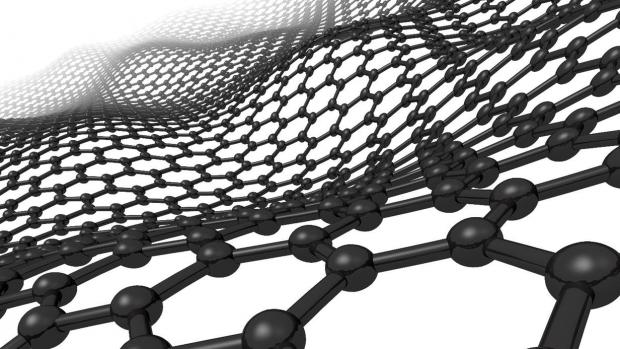
By tapping into the random fluctuations of the carbon atoms that make up graphene sheets, the scientists can generate an alternating current strong enough to indefinitely power a wristwatch.
Graphene is a lattice of carbon just one atom thick, and its incredible strength and conductivity of electricity and heat mean it might soon start cropping up in everything from light bulbs to dental fillings, microphones, motorbike helmets, water filters, smartphone screens and even heat-dissipating shoes.
The University of Arkansas researchers stumbled onto a new potential use for the material, when they set out to study the innate movements of graphene using a scanning tunneling microscope. In a phenomenon called Brownian motion, particles suspended in a fluid will randomly move in response to collisions with larger particles in the environment. In the case of a sheet of graphene, the atoms vibrate in response to the temperature around them, making sections of the linked carbon atoms rise and fall like waves on the ocean, sending ripples running through the material.

 X BANS AI War Videos
X BANS AI War Videos


