
Breaking News
 Poland to Buy 150 Tons More Gold, Approves up to 36.6% Held
Poland to Buy 150 Tons More Gold, Approves up to 36.6% Held
 Michael Oliver: T-Bond Nuclear Panic Will Send Silver VIOLENTLY to $300–$500 | Gold to $8,000
Michael Oliver: T-Bond Nuclear Panic Will Send Silver VIOLENTLY to $300–$500 | Gold to $8,000
 Greentanamo: Trump Deal Gives US Sovereignty Over Small Pockets Of Greenland For Military Bases
Greentanamo: Trump Deal Gives US Sovereignty Over Small Pockets Of Greenland For Military Bases
 Das: Trump's Spat With The Fed Is Not About Central Bank Independence
Das: Trump's Spat With The Fed Is Not About Central Bank Independence
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
DNA nanobot created that performs nanomechanical tasks
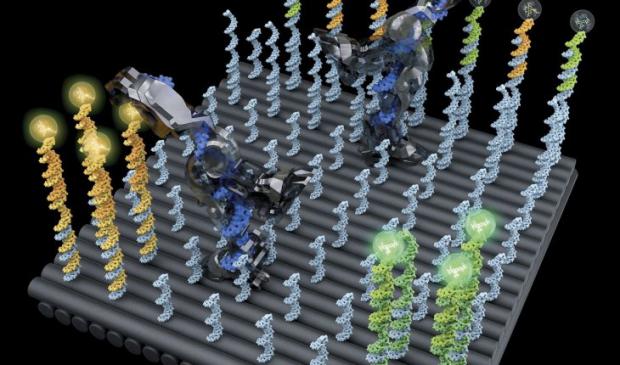
Robots are an important type of molecular machine that automatically carry out complex nanomechanical tasks. DNA molecules are excellent materials for building molecular robots, because their geometric, thermodynamic, and kinetic properties are well understood and highly programmable. So far, the development of DNA robots has been limited to simple functions. Most DNA robots were designed to perform a single function: walking in a controlled direction. A few demonstrations included a second function combined with walking (for example, picking up nanoparticles or choosing a path at a junction). However, these relatively more complex functions were also more difficult to control, and the complexity of the tasks was limited to what the robot can perform within 3 to 12 steps. In addition, each robot design was tailored for a specific task, complicating efforts to develop new robots that perform new tasks by combining functions and mechanisms.

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


