
Breaking News
 The Pentagon Failed Its Audit Again. You Should Be Alarmed.
The Pentagon Failed Its Audit Again. You Should Be Alarmed.
 Cuban Crisis 2.0. What if 'Gerans' flew from Cuba?
Cuban Crisis 2.0. What if 'Gerans' flew from Cuba?
 Senate Democrats Offer Promising Ideas for Changing Immigration Enforcement
Senate Democrats Offer Promising Ideas for Changing Immigration Enforcement
 Never Seen Risk Like This Before in My Career
Never Seen Risk Like This Before in My Career
Top Tech News
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
 Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
 New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
 Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Stay cool without electricity:
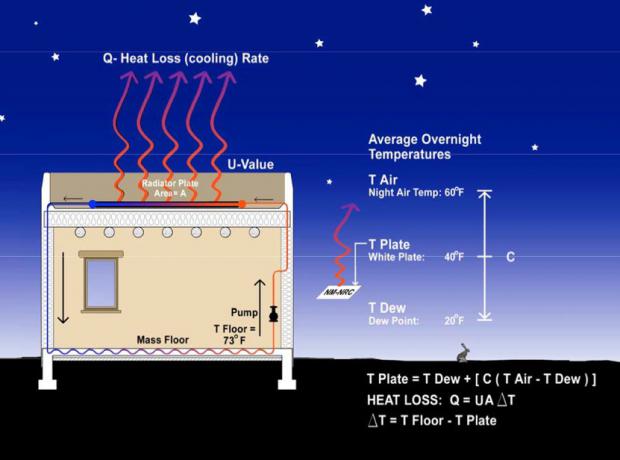
Staying cool during hot or humid weather without racking up a hefty electricity bill could be a reality in the near future. A team of researchers from Stanford University have developed a passive cooling system that sends excess heat towards outer space. Since almost no energy is required to keep them functional, these high-tech optical surfaces could one day help reduce the amount of electricity being consumed by air conditioners and refrigerators.
"This research builds on our previous work with radiative sky cooling but takes it to the next level," explained Shanhui Fan, lead researcher and professor of electrical engineering. "It provides for the first time a high-fidelity technology demonstration of how you can use radiative sky cooling to passively cool a fluid and, in doing so, connect it with cooling systems to save electricity."



