
Breaking News
 Poland to Buy 150 Tons More Gold, Approves up to 36.6% Held
Poland to Buy 150 Tons More Gold, Approves up to 36.6% Held
 Michael Oliver: T-Bond Nuclear Panic Will Send Silver VIOLENTLY to $300–$500 | Gold to $8,000
Michael Oliver: T-Bond Nuclear Panic Will Send Silver VIOLENTLY to $300–$500 | Gold to $8,000
 Greentanamo: Trump Deal Gives US Sovereignty Over Small Pockets Of Greenland For Military Bases
Greentanamo: Trump Deal Gives US Sovereignty Over Small Pockets Of Greenland For Military Bases
 Das: Trump's Spat With The Fed Is Not About Central Bank Independence
Das: Trump's Spat With The Fed Is Not About Central Bank Independence
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
More durable and longer lasting lithium-ion batteries with nanosheet anodes
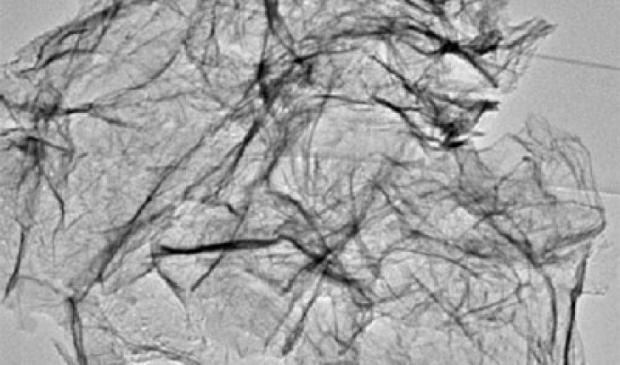
These nanosheets (image on right) are 50,000 times thinner than a sheet of paper, allowing faster charging of power compared to current battery technology. The wide surface area of the nanosheets makes better contact with the electrolyte, thus increasing the storage capacity. The material is also highly durable and does not break easily, which improves the battery shelf life. Existing methods of making metal oxide nanosheets are time-consuming and difficult to scale up.
The IBN researchers came up with a simpler and faster way to synthesize metal oxide nanosheets using graphene oxide. Graphene oxide is a 2D carbon material with chemical reactivity that facilities the growth of metal oxides on its surface.
Graphene oxide was used as the template to grow metal oxides into nanosheet structures via a simple mixing process, followed by heat treatment. The researchers were able to synthesize a wide variety of metal oxides as nanosheets, with control over the composition and properties.

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


