
Breaking News
 Is The Government Coming For Our Seeds?
Is The Government Coming For Our Seeds?
 Looming ice storm could be among worst on record
Looming ice storm could be among worst on record
 The walls are actually closing in on Ilhan Omar and her husband…
The walls are actually closing in on Ilhan Omar and her husband…
 Tesla and XAI's Digital Agent Strategy
Tesla and XAI's Digital Agent Strategy
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
IBM has made Carbon nanotubes transistors smaller and faster than silicon
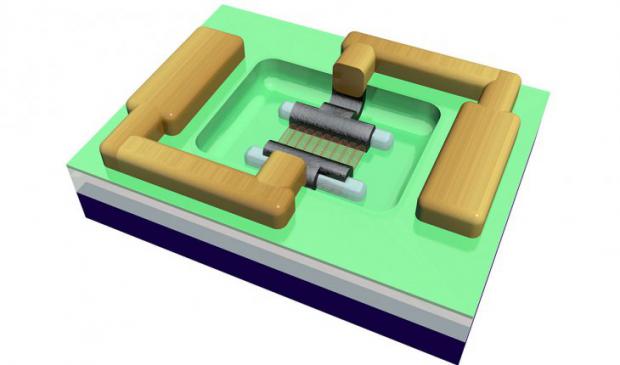
Now IBM and others will have to scale up superior carbon nanotube devices.
IBM scientists have been experimenting with carbon nanotubes, rolled-up sheets of carbon atoms just 1 nanometer, or a billionth of a meter, in diameter. But difficulties working with the material have meant that, for optimal performance, nanotube transistors have to be even larger than current silicon transistors, which are about 100 nanometers across. To cut that number down, a team of scientists used a new technique to build the contacts that draw current into and out of the carbon nanotube transistor. They constructed the contacts out of molybdenum, which can bond directly to the ends of the nanotubes, making them smaller. They also added cobalt so the bonding could take place at a lower temperature, allowing them to shrink the gap between the contacts. Another advance allowed for practical transistors.

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


