
Breaking News
Endless Opportunities on Life's Highway
THE UNCONSTITUTIONAL INCOME TAX
 WOW: Schumer now privately BEGGING to reopen the Gov – Liberal Hivemind
WOW: Schumer now privately BEGGING to reopen the Gov – Liberal Hivemind
 Obamacare's Devastating Legacy: Skyrocketing Costs, Useless Coverage, and Windfall Profits...
Obamacare's Devastating Legacy: Skyrocketing Costs, Useless Coverage, and Windfall Profits...
Top Tech News
 Future of Satellite of Direct to Cellphone
Future of Satellite of Direct to Cellphone
 Amazon goes nuclear with new modular reactor plant
Amazon goes nuclear with new modular reactor plant
 China Is Making 800-Mile EV Batteries. Here's Why America Can't Have Them
China Is Making 800-Mile EV Batteries. Here's Why America Can't Have Them
 China Innovates: Transforming Sand into Paper
China Innovates: Transforming Sand into Paper
 Millions Of America's Teens Are Being Seduced By AI Chatbots
Millions Of America's Teens Are Being Seduced By AI Chatbots
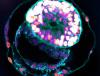 Transhumanist Scientists Create Embryos From Skin Cells And Sperm
Transhumanist Scientists Create Embryos From Skin Cells And Sperm
 You've Never Seen Tech Like This
You've Never Seen Tech Like This
 Sodium-ion battery breakthrough: CATL's latest innovation allows for 300 mile EVs
Sodium-ion battery breakthrough: CATL's latest innovation allows for 300 mile EVs
 Defending Against Strained Grids, Army To Power US Bases With Micro-Nuke Reactors
Defending Against Strained Grids, Army To Power US Bases With Micro-Nuke Reactors
Theoretical "supersolid" state of matter created in two separate studies
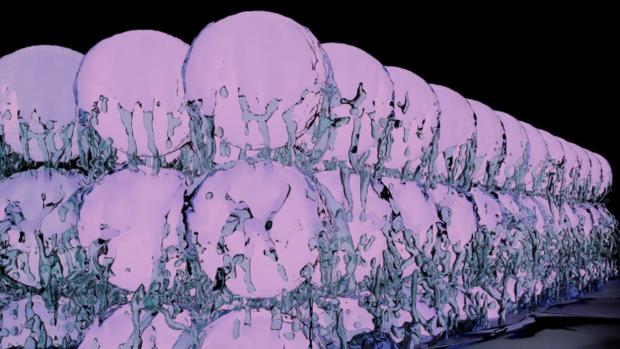
Now one such state, first proposed almost 50 years ago, has been created in experiments for the first time. Say hello to the supersolid, a state where atoms simultaneously exhibit a crystalline structure but still flow like a frictionless fluid.
The concept of a supersolid arose from the Nobel Prize-winning discovery in the 1970s of a superfluid, a liquid that has zero viscosity, meaning it flows with no resistance or "thickness." At the time, British physicist David Thouless theorized that a state of matter could exist where atoms are both free flowing like a superfluid, but also arranged in a crystalline structure, making it a supersolid.
Earlier attempts to produce this state used helium, the element that first exhibited superfluidity, but it was never brought to fruition. Now, two simultaneous – but independent – studies, one from ETH Zurich and one from MIT, have produced supersolids from Bose-Einstein condensates, using two different techniques.

 SpaceX Heat Shield and Starship Mass Production
SpaceX Heat Shield and Starship Mass Production

