
Breaking News
 Is The Government Coming For Our Seeds?
Is The Government Coming For Our Seeds?
 Looming ice storm could be among worst on record
Looming ice storm could be among worst on record
 The walls are actually closing in on Ilhan Omar and her husband…
The walls are actually closing in on Ilhan Omar and her husband…
 Tesla and XAI's Digital Agent Strategy
Tesla and XAI's Digital Agent Strategy
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
Nanostructured electrode could boost lithium battery storage by 50%
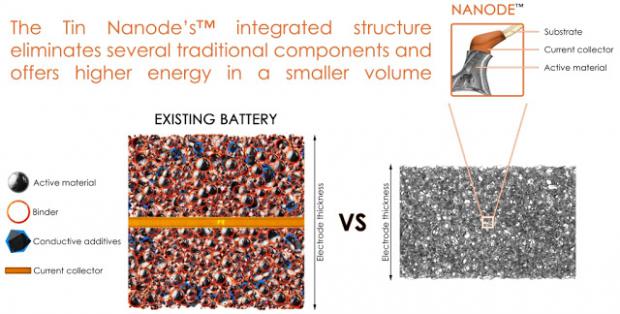
This allows the batteries to last longer between charges while also charging faster. These achievements are due to both the material structure and the use of tin as the active material. Tin is known to have much higher energy density than the current graphite technology, but until now its commercial success has been limited due to its tendency to swell during charging, causing stress in the electrode material and leading to a rapid loss in energy. Current commercial lithium ion batteries employ a foil/particle system as the electrode structure. The capability of such electrodes to deal with volume expansion of high energy materials is limited, because as the particles swell, the electrode expands.
The Tin Nanode's™ integrated electrode structure contributes to the relaxation of stress associated with electrode materials undergoing high volume expansion. This is possible because thin films of active material are spread over a 3D and porous network of fibres, rather than stacking particles on a flat copper foil.

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


