Breaking News
 Is The Government Coming For Our Seeds?
Is The Government Coming For Our Seeds?
 Looming ice storm could be among worst on record
Looming ice storm could be among worst on record
 The walls are actually closing in on Ilhan Omar and her husband…
The walls are actually closing in on Ilhan Omar and her husband…
 Tesla and XAI's Digital Agent Strategy
Tesla and XAI's Digital Agent Strategy
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
Semiconductor for next generation power electronics
The semiconductor is promising for next-generation "power electronics," or devices needed to control the flow of electrical energy in circuits. Such a technology could help to reduce global energy use and greenhouse gas emissions by replacing less efficient and bulky power electronics switches now in use.
The transistor, called a gallium oxide on insulator field effect transistor, or GOOI, is especially promising because it possesses an "ultra-wide bandgap," a trait needed for switches in high-voltage applications.
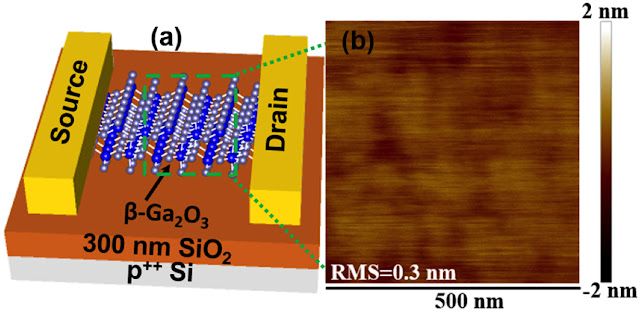
The schematic at left shows the design for an experimental transistor made of a semiconductor called beta gallium oxide, which could bring new ultra-efficient switches for applications such as the power grid, military ships and aircraft. At right is an atomic force microscope image of the semiconductor. (Purdue University image/Peide Ye
ompared to other semiconductors thought to be promising for the transistors, devices made from beta gallium oxide have a higher "breakdown voltage," or the voltage at which the device fails, said Peide Ye, Purdue University's Richard J. and Mary Jo Schwartz Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering.
Findings are detailed in a research paper published this month in IEEE Electron Device Letters. Graduate student Hong Zhou performed much of the research.

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market