
Breaking News
 Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
 Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
 The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
 Israeli Prime Minister, Netanyahu will meet with Trump on Wednesday and deliver instructions...
Israeli Prime Minister, Netanyahu will meet with Trump on Wednesday and deliver instructions...
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Scar-free wound healing could be on its way
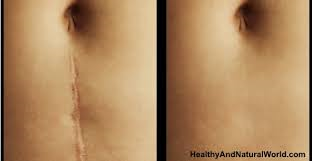
Recently, though, scientists from the University of Pennsylvania and the University of California, Irvine succeeded in addressing both factors. They're now able to get wounds to heal with regenerated skin, instead of with scar tissue.
Myofibroblasts are the most common type of cell found in healing wounds, and they're associated with scar formation. Led by U Penn's Dr. George Cotsarelis, the research team was able to get those cells to transform into ones known as adipocytes – these are the fat cells that are present in normal skin, but absent in scars.
Scientists in the Cotsarelis Lab already knew which growth factors were necessary for hair follicles to form in the skin. This knowledge previously allowed them to induce follicles to grow at wound sites on mice, although that would supposedly only be solving half of the problem.



