
Breaking News
 Brand New Solar Battery With THIS Amazing Feature! EG4 314Ah Wall Mount Review
Brand New Solar Battery With THIS Amazing Feature! EG4 314Ah Wall Mount Review
 This New Forecast Just Got WAY Worse...
This New Forecast Just Got WAY Worse...
 S3E4: The Freedom Movement Funded Its Own Prison
S3E4: The Freedom Movement Funded Its Own Prison
 Dan Bongino Gets DESTROYED By Dave Smith & Ducks Debate!
Dan Bongino Gets DESTROYED By Dave Smith & Ducks Debate!
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
Researchers Use World's Smallest Diamonds to Make Wires Three Atoms Wide...
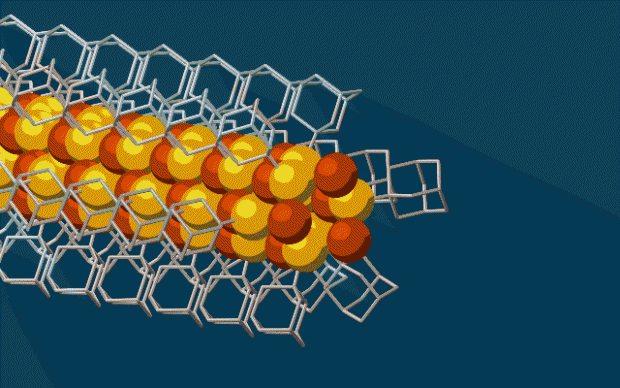
By grabbing various types of atoms and putting them together LEGO-style, the new technique could potentially be used to build tiny wires for a wide range of applications, including fabrics that generate electricity, optoelectronic devices that employ both electricity and light, and superconducting materials that conduct electricity without any loss. The scientists reported their results today in Nature Materials.
"What we have shown here is that we can make tiny, conductive wires of the smallest possible size that essentially assemble themselves," said Hao Yan, a Stanford postdoctoral researcher and lead author of the paper. "The process is a simple, one-pot synthesis. You dump the ingredients together and you can get results in half an hour. It's almost as if the diamondoids know where they want to go."

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


