
Breaking News
 Brand New Solar Battery With THIS Amazing Feature! EG4 314Ah Wall Mount Review
Brand New Solar Battery With THIS Amazing Feature! EG4 314Ah Wall Mount Review
 This New Forecast Just Got WAY Worse...
This New Forecast Just Got WAY Worse...
 S3E4: The Freedom Movement Funded Its Own Prison
S3E4: The Freedom Movement Funded Its Own Prison
 Dan Bongino Gets DESTROYED By Dave Smith & Ducks Debate!
Dan Bongino Gets DESTROYED By Dave Smith & Ducks Debate!
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
Researchers at Japan Tokai University found a room temperature Superconductor ---
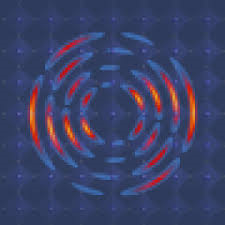
Researchers at Tokai University have created materials obtained by bringing n-alkanes into contact with graphite which are capable of conducting electricity with almost no energy loss at room temperature. They report that the sudden jump in resistance showing a phase transition is observed in the materials during heating by two-probe resistance measurement. The measured critical temperatures of the materials consisting of pitch-based graphite fibers and n-alkanes having 7-16 carbon atoms range from 363.08 to 504.24 K (231 Celsius) and the transition widths range between 0.15 and 3.01 K. They also demonstrate that superconductors with critical temperatures beyond 504 K (231 Celsius) are obtained by alkanes with 16 or more carbon atoms.
In 1986, a cuprate superconductor (Ba-La-Cu-O system) having a critical temperature which goes over the BCS limit (~30 K) was discovered and then a cuprate superconductor (Y-Ba-Cu-O system) with a critical temperature higher than 77 K was discovered. Furthermore, a Hg-based cuprate with a critical temperature of 133 K was found. The 133 K is still the highest critical temperature of conventional superconductors under atmospheric pressure

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


