
Breaking News
How Do Dumb People or Corrupt People Get Elected to Top Positions?
 Brand New Solar Battery With THIS Amazing Feature! EG4 314Ah Wall Mount Review
Brand New Solar Battery With THIS Amazing Feature! EG4 314Ah Wall Mount Review
 This New Forecast Just Got WAY Worse...
This New Forecast Just Got WAY Worse...
 S3E4: The Freedom Movement Funded Its Own Prison
S3E4: The Freedom Movement Funded Its Own Prison
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
Liquid light switch bridges the gap between light and electricity
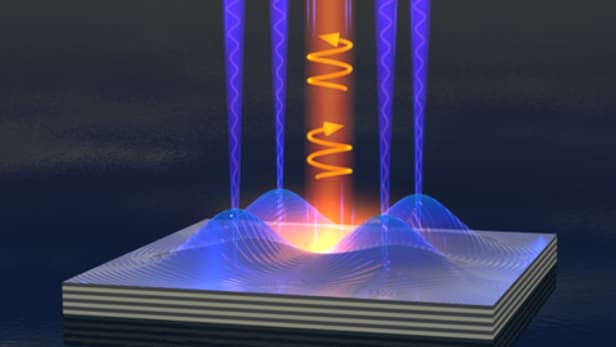
Scientists working at the University of Cambridge have used a form of liquid light to create a semiconductor switch that is so small that it not only blurs the distinction between light and electricity, but could also enable the development of much faster and smaller electronic components well into the future.
With the limits of Moore's Law looming closer day by day, the demand for faster, smaller electronics ever increasing, and microelectronics reaching the point where quantum effects are seriously challenging the continued use of electrons as a transporter of data, researchers the world over are exploring ways to solve these problems.
With contemporary methods used to convert between electrical signals and optical ones considered largely inefficient, University of Cambridge researchers believe that it would be better simply to cut out the middleman and mix the two together. In a quest to achieve this, the researchers created a switch using a new state of matter known as a Polariton Bose-Einstein condensate to combine electric and optical signals, while consuming infinitesimally small quantities of energy in the process.

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


