
Breaking News
How Do Dumb People or Corrupt People Get Elected to Top Positions?
 Brand New Solar Battery With THIS Amazing Feature! EG4 314Ah Wall Mount Review
Brand New Solar Battery With THIS Amazing Feature! EG4 314Ah Wall Mount Review
 This New Forecast Just Got WAY Worse...
This New Forecast Just Got WAY Worse...
 S3E4: The Freedom Movement Funded Its Own Prison
S3E4: The Freedom Movement Funded Its Own Prison
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
Light is information's new friend: 100x increase in amount of information 'packed into light
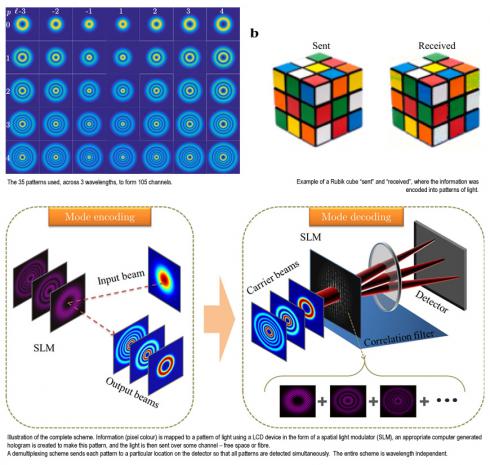
A research team demonstrates over 100 patterns of light used in an optical communication link, potentially increasing the bandwidth of communication systems by 100 times.
The rise of big data and advances in information technology has serious implications for our ability to deliver sufficient bandwidth to meet the growing demand.
Researchers at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg, South Africa, and the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) are looking at alternative sources that will be able to take over where traditional optical communications systems are likely to fail in future.
In their latest research, published online today (10 June 2016) in the scientific journal, Scientific Reports, the team from South Africa and Tunisia demonstrate over 100 patterns of light used in an optical communication link, potentially increasing the bandwidth of communication systems by 100 times.
The idea was conceived by Professor Andrew Forbes from Wits University, who led the collaboration. The key experiment was performed by Dr Carmelo Rosales-Guzman, a Research Fellow in the Structured Light group in the Wits School of Physics, and Dr Angela Dudley of the CSIR, an honorary academic at Wits.
The first experiments on the topic were carried out by Abderrahmen Trichili of Sup'Com (Tunisia) as a visiting student to South Africa as part of an African Laser Centre funded research project. The other team members included Bienvenu Ndagano (Wits), Dr Amine Ben Salem (Sup'Com) and Professor Mourad Zghal (Sup'Com), all of who contributed significantly to the work.
Bracing for the bandwidth ceiling....

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


