
Breaking News
 The Famine Years: How Trump's Unnecessary War Has Put Global Food Security on the Brink
The Famine Years: How Trump's Unnecessary War Has Put Global Food Security on the Brink
 The Myth of Fed Independence--and How to Actually Stop the Inflation Machine
The Myth of Fed Independence--and How to Actually Stop the Inflation Machine
 Interview 2007 – Iran War Oil Crunch Plunges World Into Crisis (NWNW #622)
Interview 2007 – Iran War Oil Crunch Plunges World Into Crisis (NWNW #622)
 BEWARE: AI's New Role in Election Fraud
BEWARE: AI's New Role in Election Fraud
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Embedded nanoparticles clear the way for smart glass devices
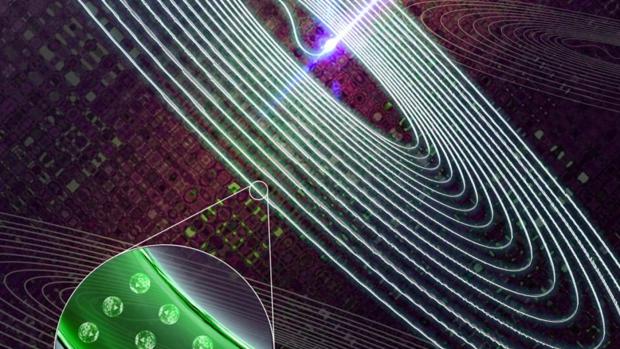
Able to be molded in almost any shape, and even extruded into optical fibers, the researchers claim that this new "hybrid glass" could be used to create new smart glass devices, including smart 3D displays and remote radiation sensors.
Australian researchers at the University of Adelaide, in collaboration with Macquarie University and the University of Melbourne, created this glowing glass by molding upconversion luminescent nanoparticles directly into the translucent material using a two-temperature glass-melting technique. The embedded nanoparticles produce luminescence when two or more low-energy, longer wavelength (usually infrared) photons are absorbed by the particles which then emit a single higher-energy, shorter wavelength photon in return.
"These novel luminescent nanoparticles, called upconversion nanoparticles, have become promising candidates for a whole variety of ultra-high tech applications such as biological sensing, biomedical imaging and 3D volumetric displays," says Dr Tim Zhao, from the University of Adelaide's School of Physical Sciences and Institute for Photonics and Advanced Sensing (IPAS). "Integrating these nanoparticles into glass, which is usually inert, opens up exciting possibilities for new hybrid materials and devices that can take advantage of the properties of nanoparticles in ways we haven't been able to do before."

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

