
Breaking News
How Do Dumb People or Corrupt People Get Elected to Top Positions?
 Brand New Solar Battery With THIS Amazing Feature! EG4 314Ah Wall Mount Review
Brand New Solar Battery With THIS Amazing Feature! EG4 314Ah Wall Mount Review
 This New Forecast Just Got WAY Worse...
This New Forecast Just Got WAY Worse...
 S3E4: The Freedom Movement Funded Its Own Prison
S3E4: The Freedom Movement Funded Its Own Prison
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
PHONE CAMERAS COULD GET AS SHARP AS DSLRS, BY BENDING LAWS OF NATURE
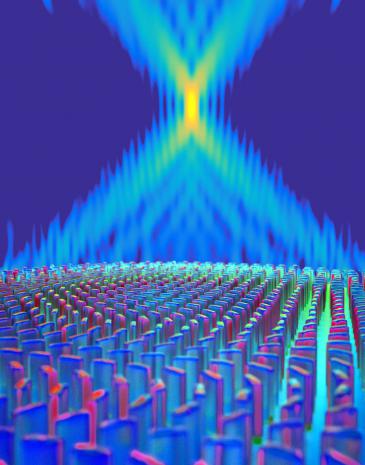
A new grain-of-sand-sized lens could one day compete with those enormous DSLR lenses to create sharp pictures.
A group of scientists at Harvard University debuted their new "metalens" in Science last week, and hope it will have applications in all sorts of imaging, from photography to other optics like microscopes and telescopes. These lenses aren't just smaller, measuring in at just 2 millimeters in diameter, but potentially much cheaper than the lenses the industry uses today.
"We wanted to replace bulky optics," Mohammadreza Khorasaninejad, first author on the study, told Popular Science. "We can reduce the cost to 2 or 3 orders of magnitude."

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


