
Breaking News
Importing Poverty into America: Devolving Our Nation into Stupid
 Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
 Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
 The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Repairing damaged cartilage with a man-made bio-glass
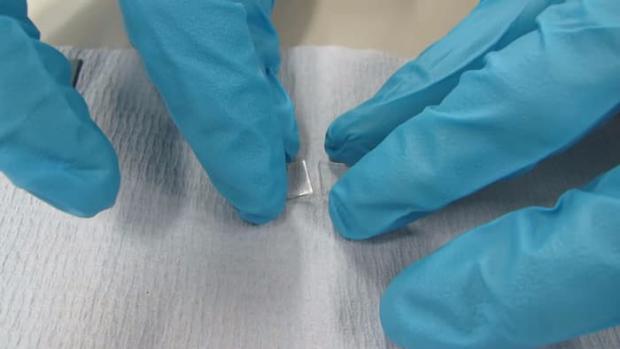
Cartilage, which is found in joints, as well as between vertebrae in the spine, is not as easy to repair as other types of connective tissue, and its degeneration can leave patients in a lot of pain. A new bio-material, made up of a mixture of a polymer called polycaprolactone and silica, could help with the ability to replace lost cartilage.
It's similar to real cartilage in that it's strong, flexible and durable, giving it the same load-bearing and shock-absorbing properties. Furthermore, it's possible to produce the material in a biodegradable ink form, allowing researchers to 3D print structures. The material also has self-healing properties, allowing two sections to firmly reattach after being pulled apart.
The researchers believe that the material could be useful in numerous situations. For example, it could be used to create implants for patients with damaged intervertebral discs, or to 3D print tiny biodegradable scaffolds that replicate lost cartilage in the knee.



