
Breaking News
Importing Poverty into America: Devolving Our Nation into Stupid
 Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
 Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
 The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Gene Therapy For Congenital Blindness Has Long-Lasting Effect
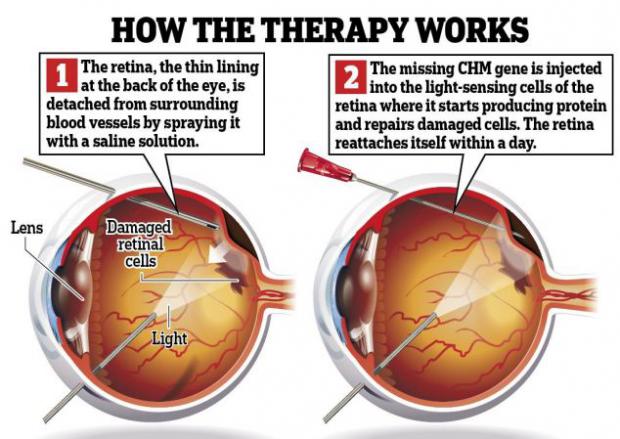
For the one in 50,000 people born with the genetic disorder choroideremia, there's no treatment that can slow the progressive vision loss. Scientists from the University of Oxford have been developing a gene therapy treatment to reverse the effects of the disease, and, though the initial results seemed promising, they had not been sure the treatment would work in the long term.
According to a study published today in the New England Journal of Medicine, the treatment has worked well in patients over the course of four years, buoying hopes that treatment for the condition (and for other genetic degenerative eye conditions like retinitis pigmentosa or macular degeneration) may become available to other patients soon.
Many gene therapy treatments have been focused on conditions that affect the eyes. These diseases are often caused by just one or two genes, the eyes are easy to access to administer the treatment, and results are often easy to detect by comparing a patient's treated and untreated eyes.



