
Breaking News
 The Prostate Cancer Test Dilemma
The Prostate Cancer Test Dilemma
 The Separation of Righteousness and Politics
The Separation of Righteousness and Politics
 Russian strike knocks out power in Kyiv FRANCE 24 English
Russian strike knocks out power in Kyiv FRANCE 24 English
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Robotic Hand with Bones, Ligaments and Tendons Created for First Time Using 3D Printing
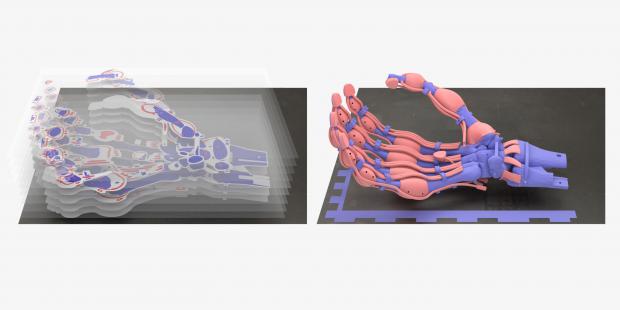
The various polymers can be fine-tuned to replicate the elasticity or rigidity of a human hand, representing a major advancement over existing 3D-printed prosthetics.
While 3D printing technology was previously limited to fast-curing plastics, researchers have now made it suitable for slow-curing plastics as well.
They say these materials have "decisive" advantages as they have enhanced elastic properties and are more durable and robust.
The use of such polymers is made possible by new technology developed by researchers at ETH Zurich in Switzerland and a US startup from Mass. Institute of Technology which can be used to create delicate structures and parts with cavities as desired. InkBit from MIT now offers the technology and prints complex objects on customer request.The technology also makes it easy to combine soft, elastic, and rigid materials.
"We wouldn't have been able to make this hand with the fast-curing polyacrylates we've been using in 3D printing so far," said Thomas Buchner, a doctoral student from ETH Zurich who led the authorship of the paper published on their work.
"We're now using slow-curing thiolene polymers. These have very good elastic properties and return to their original state much faster after bending than polyacrylates," he said, adding this makes them ideal for making complex prosthetics.

 Pathway to the stars
Pathway to the stars

