
Breaking News
 EXCLUSIVE: "The HUGE Elephant In The Room Is Actually What Jeffrey Epstein Was Best At..."
EXCLUSIVE: "The HUGE Elephant In The Room Is Actually What Jeffrey Epstein Was Best At..."
 EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEW: Republican Candidate For Texas Governor "Doc" Pete Chambers Joins...
EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEW: Republican Candidate For Texas Governor "Doc" Pete Chambers Joins...
 Epstein Files Trigger Political Fallout Across Europe
Epstein Files Trigger Political Fallout Across Europe
 Conjoined twin 'influencers' who have gained more than 280,000 followers with their intimate
Conjoined twin 'influencers' who have gained more than 280,000 followers with their intimate
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
This new solar-powered device can pull water straight from the desert air
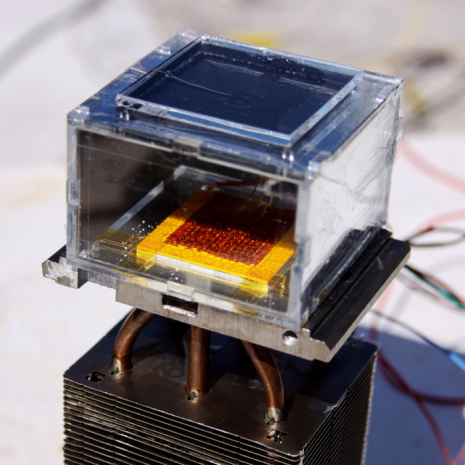
The device can produce nearly 3 liters of water per day for every kilogram of spongelike absorber it contains, and researchers say future versions will be even better. That means homes in the driest parts of the world could soon have a solar-powered appliance capable of delivering all the water they need, offering relief to billions of people.
There are an estimated 13 trillion liters of water floating in the atmosphere at any one time, equivalent to 10% of all of the freshwater in our planet's lakes and rivers. Over the years, researchers have developed ways to grab a few trickles, such as using fine nets to wick water from fog banks, or power-hungry dehumidifiers to condense it out of the air. But both approaches require either very humid air or far too much electricity to be broadly useful.



